- 10 Strategies to Overcome Insomnia
- Could Artificial Sweeteners Be Aging the Brain Faster?
- Techniques for Soothing Your Nervous System
- Does the Water in Your House Smell Funny? Here’s Why
- Can a Daily Dose of Apple Cider Vinegar Actually Aid Weight Loss?
- 6 Health Beverages That Can Actually Spike Your Blood Sugar
- Treatment Options for Social Anxiety Disorder
- Understanding the Connection Between Anxiety and Depression
- How Daily Prunes Can Influence Cholesterol and Inflammation
- When to Take B12 for Better Absorption and Energy
Lung Cancer Surgery Rates Differ Widely Between States
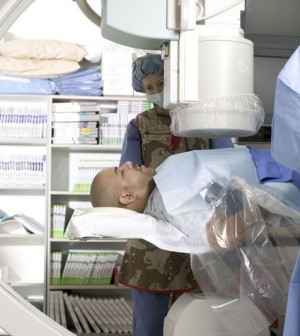
Rates of surgery to cure lung cancer vary greatly across the United States, a new study finds.
Researchers analyzed data from patients in 38 states and the District of Columbia who were diagnosed with early stage non-small cell lung cancer between 2007 and 2011.
Non-small cell lung cancer is the most common type of lung cancer. It can potentially be cured by surgery if it’s detected at an early stage before it spreads, the study authors pointed out.
The highest rates of surgery to cure lung cancer were seen in Massachusetts, New Jersey and Utah, at about 75 percent each. The lowest rate was in Wyoming, where patients were 25 percent less likely to have curative surgery than those in the top three states, the findings showed.
“We do not have a uniform quality of health care in this country,” said Dr. Helmneh Sineshaw, health services researcher with the American Cancer Society. “Curative surgery for non-small cell lung cancer is one example.”
The other states with the lowest rates of curative surgery included: Colorado, Louisiana, New Mexico, Oklahoma and Texas, according to the study.
The report was scheduled for presentation Friday at an American Association for Cancer Research meeting in Atlanta. Research presented at meetings should be considered preliminary until published in a peer-reviewed medical journal.
States with major medical centers generally had higher rates of lung cancer surgery. Also, insurance may play a role in the differences among states, Sineshaw suggested in an association news release.
“From state to state, the quality of insurance coverage may be different, even as we move toward universal health care. Varying standards for co-pays, for example, can all add up and make a difference in the cost of treatment,” he said.
One potential solution would be to further standardize health care coverage, Sineshaw said.
More information
The U.S. National Cancer Institute has more about non-small cell lung cancer.
Source: HealthDay
Copyright © 2026 HealthDay. All rights reserved.










