- Comparing Whey and Plant-Based Protein: Which is Best?
- How Long Does Nicotine Remain in Your System?
- The Best Time of Day to Drink Bone Broth to Maximize Health Benefits
- 8 Ways to Increase Dopamine Naturally
- 7 Best Breads for Maintaining Stable Blood Sugar
- Gelatin vs. Collagen: Which is Best for Skin, Nails, and Joints?
- The Long-Term Effects of Daily Turmeric Supplements on Liver Health
- Could Your Grocery Store Meat Be Causing Recurring UTIs?
- Are You Making This Expensive Thermostat Error This Winter?
- Recognizing the Signs of Hypothyroidism
Seniors Often Underestimate Their Frailty, Study Finds
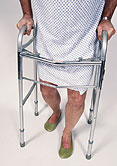
Many American seniors seen at emergency departments overestimate their mobility, according to a recent study.
Researchers asked seniors who visited an ER to get out of bed, walk 10 feet and return to bed. The investigators found that almost one-quarter of these patients inaccurately assessed their ability to complete these tasks.
Of those who said they could do the tasks without assistance, 12 percent required some help or were unwilling to complete the tasks. Of those who said they could do the tasks without a cane or walker, 48 percent required some help or were unable to complete the tasks, the investigators found.
Of the seniors who said they could do the tasks with some assistance from another person, 24 percent were unable to do so even with someone helping them, the study revealed.
The findings were published online recently in the journal Annals of Emergency Medicine.
“Ensuring that older adults discharged from the emergency department are able to safely function in their home environment is important because those who are unable to function safely at home are at risk for falls and return ER visits,” lead author Dr. Timothy Platts-Mills, of the University of North Carolina, Chapel Hill, said in a news release from the American College of Emergency Physicians.
Each year, 20 million people aged 65 and older visit emergency departments in the United States, the researchers said. That number is expected to rise as baby boomers continue to age.
Platts-Mills said ER doctors are experts in deciding who can go home and who needs to stay in the hospital. But, sometimes they make these decisions based on what patients say instead of a direct assessment of ability.
“Our results suggest that patient statements are sometimes inaccurate, and, particularly for older adults who need some assistance, directly observing the patient’s ambulation can be informative. Of course being able to move around isn’t the only determinant of whether an older adult can be safely sent home, but it is a critical piece of information and it’s good to get it right,” he concluded.
More information
The AGS Foundation for Health in Aging has more about seniors and mobility problems.
Source: HealthDay
Copyright © 2026 HealthDay. All rights reserved.










