- Gelatin vs. Collagen: Which is Best for Skin, Nails, and Joints?
- The Long-Term Effects of Daily Turmeric Supplements on Liver Health
- Could Your Grocery Store Meat Be Causing Recurring UTIs?
- Are You Making This Expensive Thermostat Error This Winter?
- Recognizing the Signs of Hypothyroidism
- 10 Strategies to Overcome Insomnia
- Could Artificial Sweeteners Be Aging the Brain Faster?
- Techniques for Soothing Your Nervous System
- Does the Water in Your House Smell Funny? Here’s Why
- Can a Daily Dose of Apple Cider Vinegar Actually Aid Weight Loss?
Digital Compass Attached to Brain Helps Blind Rats ‘See’
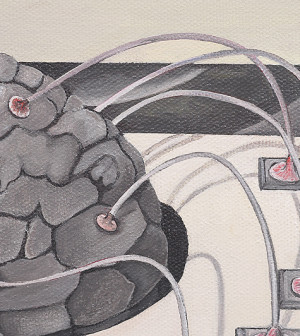

New research in rats suggests a special compass might one day help blind people navigate their physical environments.
Using a head-mounted device, Japanese scientists attached a microstimulator and a digital compass to the brains of blind rats, and those rats were then able to move through mazes nearly as well as rats with normal vision.
The compass automatically detected the rat’s head direction and generated electrical pulses that indicated which direction — such as north or south — the rat was facing.
The blind rats were then trained to seek food in a T-shaped maze or a more complicated maze. With practice, the rats learned to use the device to solve the mazes, and their performance rivaled that of rats with normal vision.
The findings suggest that a similar system could help orient blind people, the University of Tokyo researchers said. In the case of humans, the device could be attached to the canes blind people typically use for walking around, the researchers said.
It should be noted, however, that animal research findings do not always translate to humans.
The study was published April 2 in the journal Current Biology.
“We were surprised that rats can comprehend a new sense that had never been experienced or ‘explained by anybody’ and can learn to use it in behavioral tasks within only two to three days,” lead researcher Yuji Ikegaya said in a journal news release.
The results suggest that it may be possible to use such sensors to improve blind people’s mobility, the researchers added.
More information
The U.S. National Library of Medicine has more about low vision and blindness.
Source: HealthDay
Copyright © 2026 HealthDay. All rights reserved.










