- Comparing Whey and Plant-Based Protein: Which is Best?
- How Long Does Nicotine Remain in Your System?
- The Best Time of Day to Drink Bone Broth to Maximize Health Benefits
- 8 Ways to Increase Dopamine Naturally
- 7 Best Breads for Maintaining Stable Blood Sugar
- Gelatin vs. Collagen: Which is Best for Skin, Nails, and Joints?
- The Long-Term Effects of Daily Turmeric Supplements on Liver Health
- Could Your Grocery Store Meat Be Causing Recurring UTIs?
- Are You Making This Expensive Thermostat Error This Winter?
- Recognizing the Signs of Hypothyroidism
Foot Fungus on the Run … But Race Has a Long Way to Go
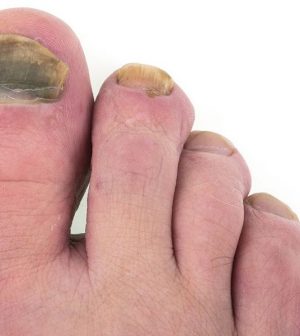
The good news is that the fungus that causes athlete’s foot and other nasty skin and toenail infections is headed for extinction.
The bad news is it could take millions of years.
Scientists analyzed samples of Trichophyton rubrum fungus and concluded it may have lost its ability to sexually reproduce as it adapted to grow on humans.
“It is commonly thought that if an organism becomes asexual, it is doomed to extinction,” said study senior author Dr. Joseph Heitman. He is chair of molecular genetics and microbiology at Duke University School of Medicine in Durham, N.C.
“While that may be true, the time frame we are talking about here is probably hundreds of thousands to millions of years,” he added in a university news release.
But this research may help uncover vulnerabilities in the fungus that could result in better medications to fight it, according to authors of the study recently published online in the journal Genetics.
About 25 percent of the world’s population have fungal infections, and T. rubrum is often to blame. It is difficult to cure and may be drug-resistant.
People can become infected when walking barefoot around swimming pools, showers or locker rooms, or when sharing personal items such as towels or nail clippers.
More information
The American Podiatric Medical Association has more on athlete’s foot.
Source: HealthDay
Copyright © 2026 HealthDay. All rights reserved.










