- Comparing Whey and Plant-Based Protein: Which is Best?
- How Long Does Nicotine Remain in Your System?
- The Best Time of Day to Drink Bone Broth to Maximize Health Benefits
- 8 Ways to Increase Dopamine Naturally
- 7 Best Breads for Maintaining Stable Blood Sugar
- Gelatin vs. Collagen: Which is Best for Skin, Nails, and Joints?
- The Long-Term Effects of Daily Turmeric Supplements on Liver Health
- Could Your Grocery Store Meat Be Causing Recurring UTIs?
- Are You Making This Expensive Thermostat Error This Winter?
- Recognizing the Signs of Hypothyroidism
Pfizer Says Lower Dose of Its COVID Vaccine Protects Younger Children
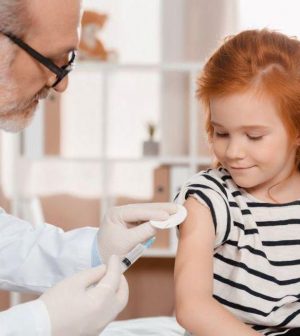
A lower dose of Pfizer’s coronavirus vaccine is 90.7% effective in preventing symptomatic COVID-19 in children aged 5 to 11, according to new clinical trial data from the company.
The data was given to the U.S. Food and Drug Administration on Friday, and the agency is expected to release its own analysis of the trial findings later in the day, The New York Times reported.
Next week, an FDA advisory panel will meet to discuss whether to recommend FDA authorization of the Pfizer vaccine for children aged 5 to 11. It’s already available for those 12 and older.
The dose used in the trial that included more than 2,200 children was 10 micrograms, while the adult dose is 30 micrograms. Twice as many study participants received the vaccine as a placebo, the Times reported.
COVID-19 was diagnosed in three children who received the vaccine and 16 of those who received the placebo, indicating it was more than 90% effective. The dosage was safe, and there were only mild side effects, according to Pfizer.
FDA authorization of the vaccine for children aged 5 to 11 could help protect more than 28 million people in the United States, according to the Times.
If the FDA does give the green light to the vaccine for that age group, the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention would then recommend how the shots should be administered.
More information
Visit the U.S. Food and Drug Administration for more on COVID vaccines.
SOURCE: The New York Times
Source: HealthDay
Copyright © 2026 HealthDay. All rights reserved.










