- Could Your Grocery Store Meat Be Causing Recurring UTIs?
- Are You Making This Expensive Thermostat Error This Winter?
- Recognizing the Signs of Hypothyroidism
- 10 Strategies to Overcome Insomnia
- Could Artificial Sweeteners Be Aging the Brain Faster?
- Techniques for Soothing Your Nervous System
- Does the Water in Your House Smell Funny? Here’s Why
- Can a Daily Dose of Apple Cider Vinegar Actually Aid Weight Loss?
- 6 Health Beverages That Can Actually Spike Your Blood Sugar
- Treatment Options for Social Anxiety Disorder
Long ICU Stays May Alter Gut Microbes

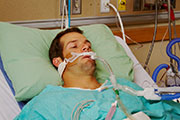
Long stays in intensive care lead to a big reduction in the types of microbes in patients’ intestines, and some of those that remain are potentially deadly, a new study indicates.
University of Chicago researchers investigated what happens to the gut microbes of intensive care unit (ICU) patients who receive repeated courses of multiple antibiotics to protect them from infection.
Patients who stayed in an ICU for longer than one month had only one to four types of microbes in the intestine, while healthy study volunteers had about 40 types, according to the study published Sept. 23 in the online journal mBio.
Some of the few remaining types of microbes in the ICU patients may increase the risk of a life-threatening systemic infection called sepsis, the researchers said.
“I have watched patients die from sepsis — it isn’t their injuries or mechanical problems that are the problem,” study co-senior author and gastrointestinal surgeon Dr. John Alverdy said in a journal news release.
“Our hypothesis has always been that the gut microflora in these patients are very abnormal, and these could be the culprits that lead to sepsis,” he added.
The findings may lead to improved monitoring and treatment of ICU patients, the researchers said.
More information
The American Thoracic Society has more about critical care.
Source: HealthDay
Copyright © 2026 HealthDay. All rights reserved.










